Look, I get it. Binary. Hexadecimal. Octal. These aren't exactly dinner table conversation topics (unless you're at a particularly nerdy dinner table, in which case—respect). But here's the thing: converting between number systems doesn't have to feel like decoding ancient hieroglyphics. This tutorial will show you how our base number converter takes that headache and just... dissolves it.
What Even Is This Tool?
Short version? It's a calculator that speaks multiple number languages.
The base number converter is a free browser tool that translates numbers between different numbering systems—binary (base-2), octal (base-8), decimal (base-10, the normal stuff we humans use), and hexadecimal (base-16, because apparently base-10 wasn't fancy enough for computer scientists). Type a number in one system, and boom—instant conversion to all the others. No math degree required, no complex formulas to memorize, no "carry the one" nonsense.
Whether you're debugging code at 2 AM (been there), studying for a computer science exam (godspeed), working with memory addresses, or just genuinely curious how the number 42 looks in binary (it's 101010, by the way—kinda satisfying), this tool has your back.
Why Would Anyone Need This?
Fair question.
If you're a developer, you've probably stumbled into situations where different number systems collide. CSS color codes use hex. Permissions in Linux use octal. Low-level programming loves binary. And sometimes you need to translate between them without pulling out a calculator and doing mental gymnastics that would make a mathematician weep.
Students hit this wall constantly—computer science courses love throwing conversions at you, and professors seem to take particular joy in making exam questions where you have to convert some absurdly large number from base-16 to base-2 while your hand cramps from writing out endless zeros and ones.
Stay in the Loop
Get notified when we add new tools and features
Thank You!
You're all set. We'll keep you updated with the latest tools and features.
System administrators deal with it when configuring permissions (chmod 755 ring any bells?). Network engineers encounter it with subnet masks. Hardware tinkerers see it when working with registers and flags. Game developers might need it for bitwise operations. The list goes on, honestly.
Getting Started With This Tutorial (It's Stupid Easy)
This tutorial starts simple. Navigate to allthethings.dev/tools/base-number-converter. That's it. No sign-ups, no downloads, no email address harvest, no "please disable your adblocker" guilt trips.
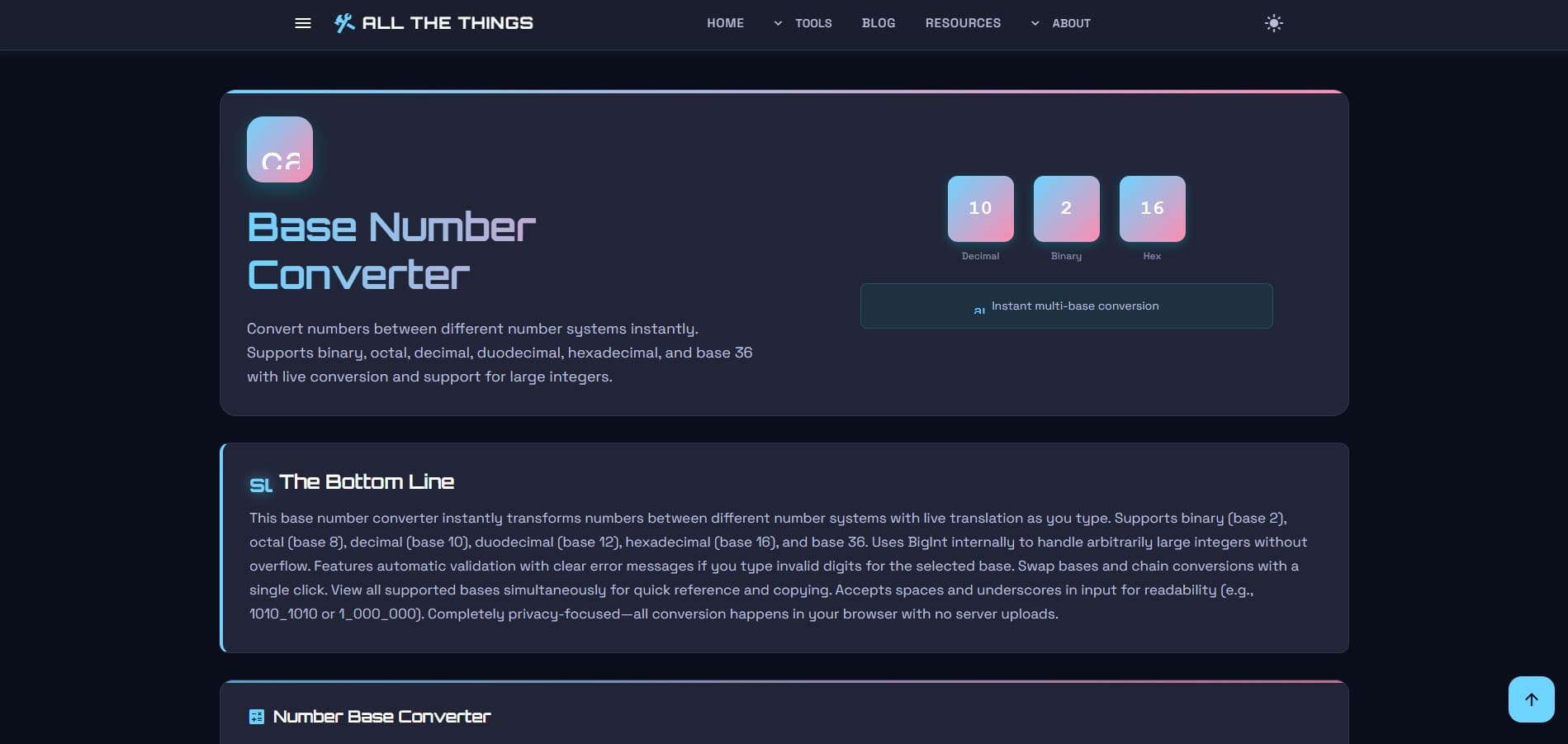
You'll see four input boxes stacked up, each representing a different number system. Binary at the top (because computers think in binary first, apparently). Then octal. Decimal in the third spot. Hexadecimal bringing up the rear.
How to Actually Use It
Here's where it gets almost comically simple.
Step 1: Pick your starting point
Got a decimal number you need in hex? Type it in the decimal box. Got a binary number that needs translation? Slap it in the binary field. Starting point doesn't matter—the tool doesn't care which direction you're converting from.
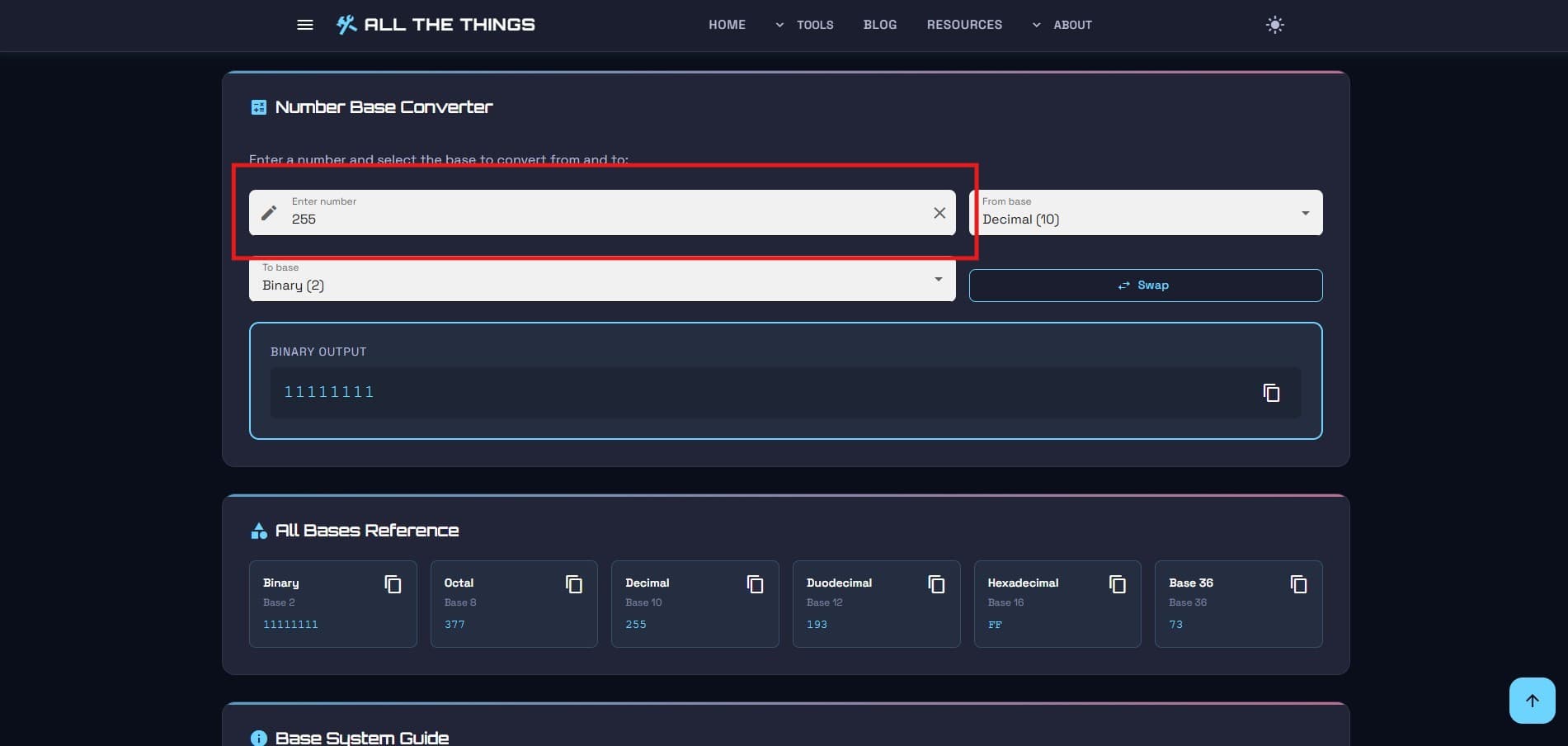
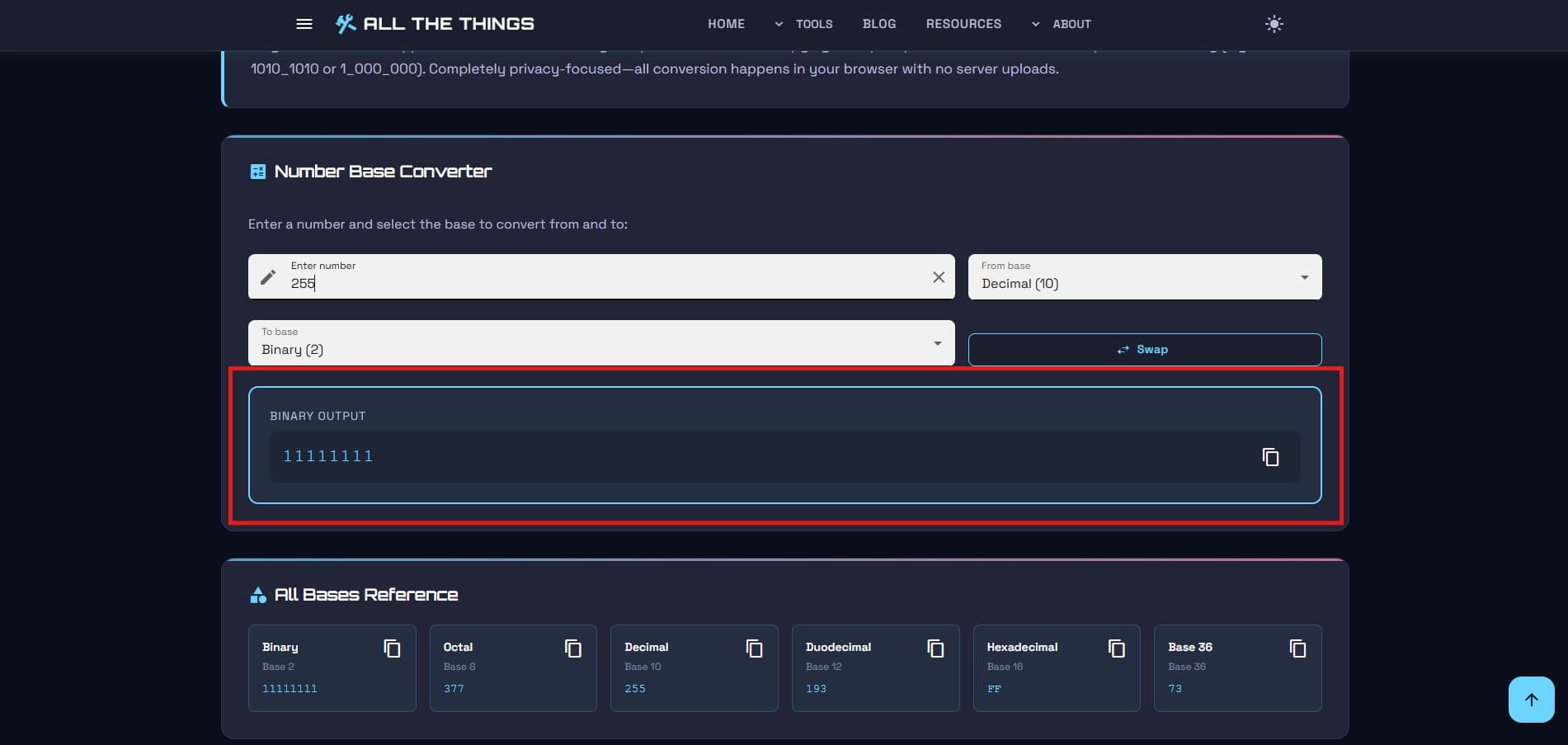
Step 2: Watch the magic happen
As you type, the other boxes fill themselves in. Real-time conversion. No submit button to click, no "calculate" to press. Just... instant results across all bases.
That's... that's honestly it. Type number, get conversions. If converting numbers were any easier, it would do your laundry too.
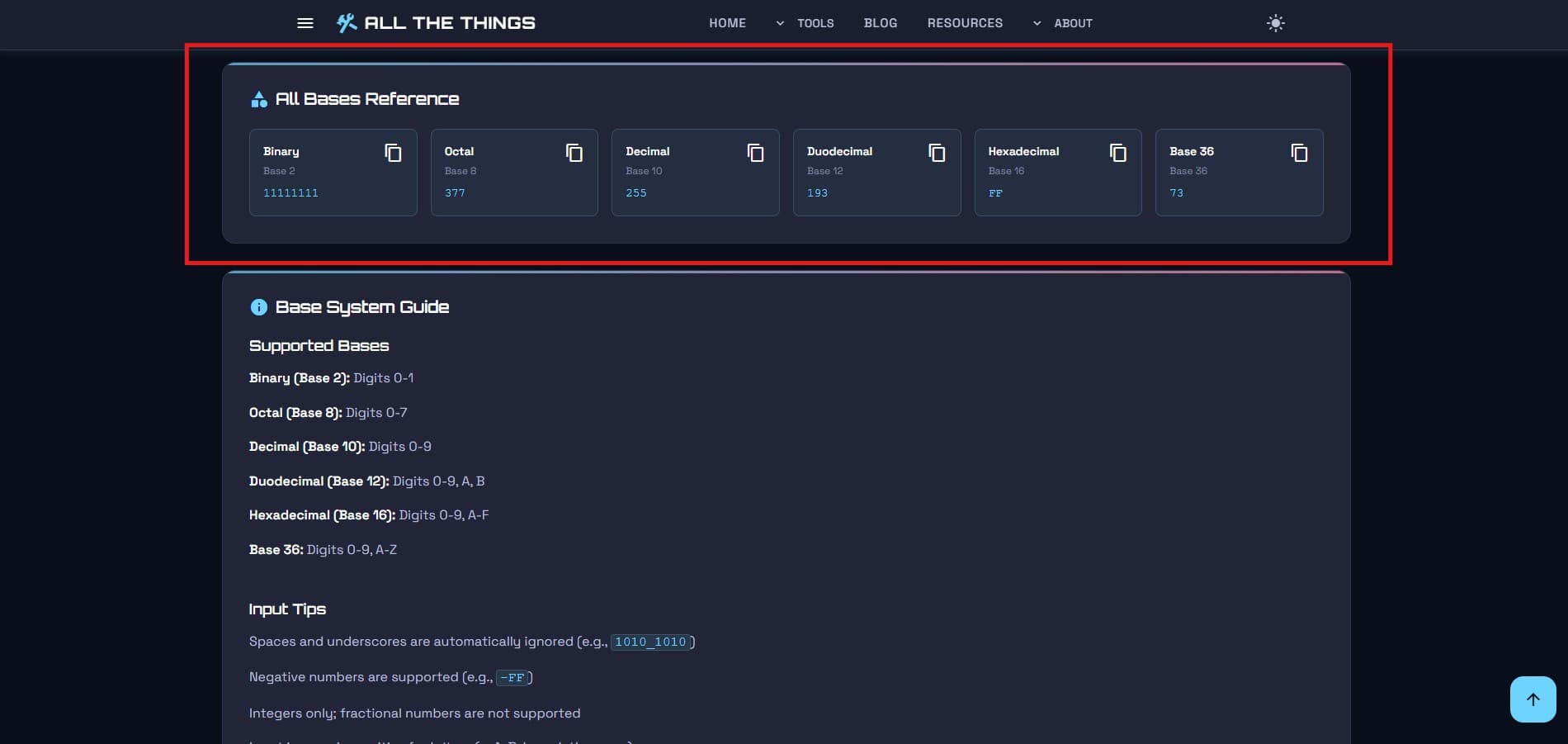
The Copy Button (Your New Best Friend)
Each conversion has a little copy button next to it. Click it. The number goes straight to your clipboard. Paste it wherever you need it—your code editor, terminal, homework assignment, angry email to your professor about why base-8 shouldn't exist (okay, maybe not that last one).
No more highlighting numbers with your cursor and hoping you didn't accidentally grab an extra space or miss a digit. One click. Done. Move on with your life.
Tutorial: Understanding What You're Actually Converting
Quick crash course for this tutorial. (Feel free to skip if you already know this stuff.)
Binary (Base-2)
Only uses 0 and 1. This is how computers think at the hardware level—electrical signals are either on (1) or off (0). Simple for circuits, tedious for humans. The number 5 in binary is 101. The number 255 is 11111111. You can see why we invented other systems.
Octal (Base-8)
Uses digits 0 through 7. Popular in the old days of computing, still shows up in Unix/Linux file permissions. When you see chmod 755, that's octal. Three digits representing permissions for owner, group, and others. Each octal digit maps neatly to three binary digits, which is why it caught on back when.
Decimal (Base-10)
This is your everyday counting system. 0-9, then you roll over to the next place value. Completely arbitrary that we use base-10, by the way—we just happen to have ten fingers. If evolution had given us eight fingers, we'd probably all be using octal and thinking decimal was weird.
Hexadecimal (Base-16)
Uses 0-9, then A-F for values 10-15. Compact way to represent binary—each hex digit maps to exactly four binary digits. Memory addresses love hex. Color codes in web design use hex (#FF0000 is red, for instance). If you've ever seen something like 0x4A2F in code, that's hex notation.
Real-World Scenarios (When You'd Actually Use This)
Debugging weird memory addresses
You're staring at a memory dump and seeing addresses like 0x7FFF. Need to know what that is in decimal to make sense of your program's behavior? Converter's got you. Paste the hex (without the 0x prefix), instantly see it's 32767 in decimal.
Understanding Linux permissions
Someone tells you to "chmod 644" a file and you want to actually understand what permissions that grants instead of just blindly copying commands from Stack Overflow. Convert 644 from octal—you'll see it's 420 in decimal, and if you convert each octal digit separately to binary, you get the read/write/execute breakdown (110 100 100 in binary, which translates to rw-r--r--).
Color code conversions
You've got RGB values (say, 127, 255, 180) and need the hex code for CSS. Convert each decimal value: 127 becomes 7F, 255 becomes FF, 180 becomes B4. Put 'em together: #7FFFB4. Boom, aqua-ish color ready for your stylesheet.
Bitwise operation sanity checks
Writing code that uses bitwise AND, OR, XOR operations and you need to verify your logic. Convert your numbers to binary, visually see the bit patterns, confirm your operations make sense before the bugs start breeding.
Homework (let's be honest)
You've got twenty conversion problems due tomorrow morning and hand-calculating each one sounds about as appealing as watching paint dry. This tutorial's tool makes homework way less painful—fire up the converter, check your work, make sure you didn't mess up carrying digits or forget a power of 2.
Tips and Tricks (The Stuff Nobody Tells You)
You can paste formatted numbers
Got a hex number with the 0x prefix? Paste it anyway. The tool strips out common prefixes and formatting automatically. Leading zeros? Fine. Spaces? It handles it. Just paste and let the tool sort it out.
Case doesn't matter for hex
Hexadecimal letters can be uppercase (A-F) or lowercase (a-f). The converter accepts both, displays uppercase by default. Type "ff" or "FF"—same result.
Clear button exists for a reason
Made a mess of conversions and want to start fresh? Hit the clear button. All fields reset. Clean slate. Sometimes starting over beats trying to edit out mistakes.
Negative numbers work too
The converter handles signed integers. Type a negative decimal number, see how it represents in other bases using two's complement notation (or however the underlying system handles it—point is, negatives work).
Bookmark it
Seriously. If you're in a field where number base conversions come up even semi-regularly, bookmark the tool. Future you will thank present you when you need a quick conversion and don't have to google "binary to hex converter" for the fifteenth time this month.
Common Conversion Patterns Worth Memorizing (Maybe)
Some conversions show up so often they're almost worth memorizing—almost. But even if you don't memorize them, seeing these patterns helps build intuition:
• 255 decimal = FF hex = 11111111 binary (all bits on in a byte, shows up constantly)
• 256 decimal = 100 hex = 100000000 binary (one more than all bits on)
• 7 octal = 111 binary (max value in 3 bits, important for permissions)
• 16 decimal = 10 hex (hex rolls over at 16, same as decimal rolls over at 10)
• Powers of 2 in binary (1, 10, 100, 1000... always a 1 followed by zeros)
But honestly? Don't stress memorizing this stuff. That's why the tool exists—so you don't have to keep lookup tables in your head like it's 1985.
When Things Get Weird
Invalid characters
Type a "9" in the octal field and watch nothing happen. Octal only goes 0-7, so the tool just ignores invalid digits. Same with binary—try typing a "2" and the field stays empty. It's not broken, it's just enforcing the rules.
Really big numbers
JavaScript (which powers the converter) can handle integers up to about 9 quadrillion (technically 2^53 - 1). Go beyond that and precision gets wonky. For normal use cases—debugging, homework, web development—you'll never hit this limit. But if you're converting astronomically large numbers, be aware things might get imprecise.
Floating point numbers
The converter handles integers. Decimal points don't translate cleanly across number bases the same way whole numbers do (that's a whole different nightmare involving fractions and approximations). Stick to whole numbers and you're golden.
Why This Tool Versus Just Googling It
Look, you could absolutely google "hex to decimal converter" every single time you need a conversion. Google will give you results. Maybe you'll get a clean tool, maybe you'll get one buried under ads, maybe you'll get one that demands you disable your adblocker or sign up for a newsletter.
This tool is clean. No nonsense. Loads fast. Works offline once cached. No tracking scripts, no "related articles" clogging the interface, no popup asking you to rate your experience. Just the converter and your numbers.
Plus, it's right here whenever you need it. Bookmark it once, never search for a converter again. Saves time. Saves sanity. Saves you from closing thirteen tabs of sketchy conversion sites.
The Bottom Line
Converting between number systems is one of those tedious tasks that computers should handle for us (ironic, since number systems exist because of computers). Whether you're elbow-deep in assembly code, configuring server permissions, designing CSS colors, or just satisfying curiosity about how binary works, having a reliable, fast, no-BS converter makes life easier.
The base number converter tutorial at allthethings.dev/tools/base-number-converter showed you a tool that does one thing and does it well: translates your numbers instantly across binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal without making you think about the math.
Because honestly, we've all got better things to do than hand-calculate powers of 16. Hope this tutorial helped.









